
Effectiveness of Qwik-Zyme D Application for Sludge Reduction in an Aerobic Digester
Independent data collected and submitted by
City of Columbus, WI
Summary
This study aims to evaluate the on-site impacts of Qwik-Zyme D, a product by Aquafix, Inc., in an aerobic digester at the Columbus, WI Wastewater Treatment Facility. Qwik-Zyme D is formulated to enhance the degradation of hard-to-degrade organic compounds and has shown promising results in boosting solids reduction in various field applications. Over a 12-week period (April 28 2024 – June 08 2024), the study was conducted using the plant’s two aerobic digesters, with the South Digester treated with Qwik-Zyme D, while the North Digester served as a control. Additionally, operational changes were made which increased the number of decants in the South Digester, allowing for longer solids retention. Weekly composite samples were collected from both digesters; laboratory analysis focused on Oxygen Uptake Rate (OUR), Total Solids (TS), and Volatile Solids (VS). Additionally, sludge loading, holding, and pressing were monitored throughout the study. The results provide insights into the efficacy of Qwik-Zyme D in improving solids reduction in aerobic digestion processes.
Background
The Columbus Wastewater Treatment Facility, located in Columbus, WI, is an extended aeration plant with two final clarifiers and tertiary treatment. The facility typically handles 0.7 to 0.9 million gallons per day (MGD), but during heavy rainfall, infiltration and inflow (1/1) can increase flows to as much as 5 MGD. The plant operates two aerobic digesters that feed into a gravity belt filter press for sludge dewatering. This study focused on optimizing solids reduction in these aerobic digesters.
Methods
A weekly composite sample was prepared by collecting approximately 200ml of sludge from each digester daily. Over five days, the daily samples from the North Digester were combined to create a 1000ml composite sample. The same process was followed for the South Digester, resulting in a 1000ml composite sample as well. These samples were picked up weekly and transported to the Aquafix, Inc. lab. These samples were evaluated for oxygen update rate, total solids, and volatile solids. Starting in Week 3 and continuing through the remainder of the 12-week study, the pounds of sludge loaded into the digesters, held in the digesters, and removed for dewatering/pressing were recorded. This data was recorded daily, and weekly averages were used for data interpretation.
Results
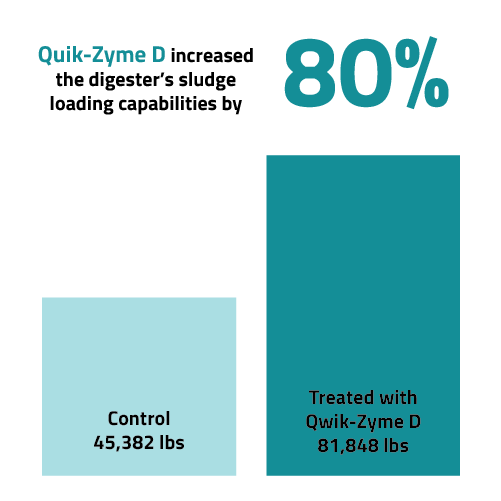
The study found that while OUR (Figure 1) and VS Percentages (Figure 2) remained similar between the North and South Digesters, the South Digester received 36,465 pounds more sludge than the North Digester (Figure 3). After 12 weeks, the total sludge loaded into each digester was compared to the total sludge removed via pressing/dewatering. Given that the sludge volumes were relatively comparable, this difference represents the amount of sludge reduced. The South Digester, treated with Qwik-Zyme D and subjected to operation changes, achieved a significant 59.85% reduction in sludge, equating to 48,984 pounds of sludge removed via biological activity. In contrast, the North Digester, which served as the control, saw only a 0.18% reduction, amounting to approximately 80 pounds of sludge removed.
Fig 1. Oxygen Uptake Rate
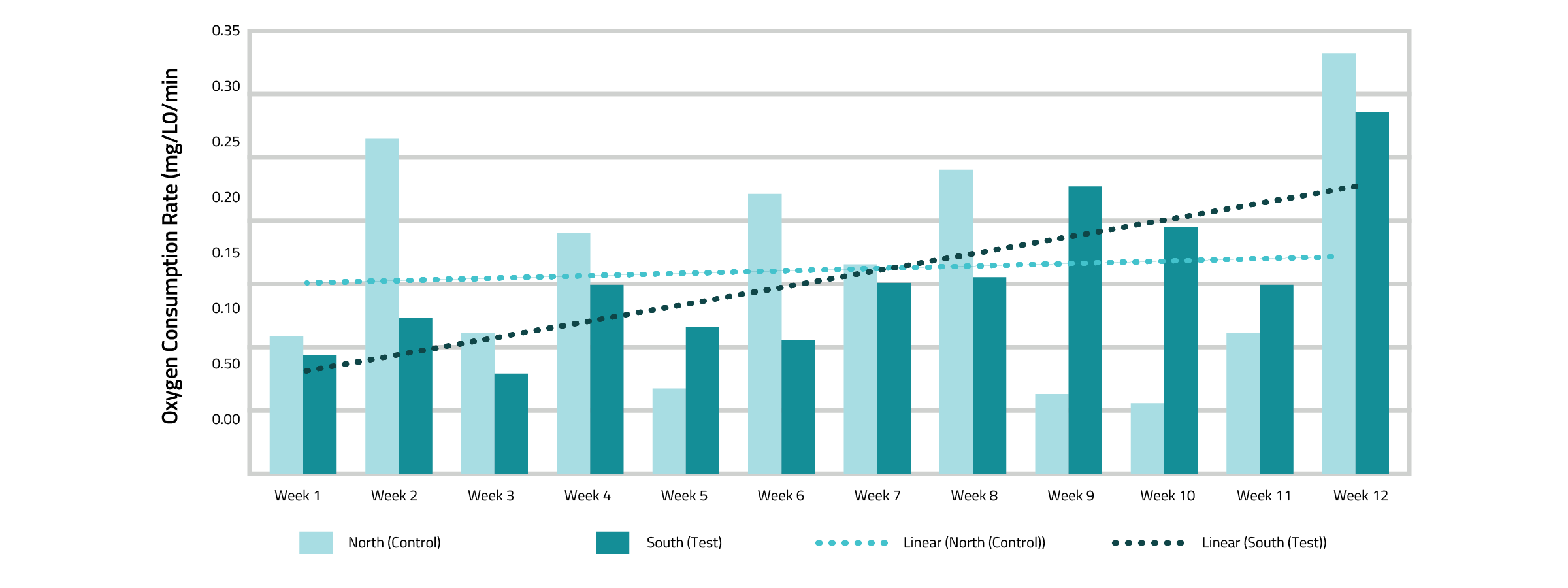
Fig 2. Percent Volatile Solids
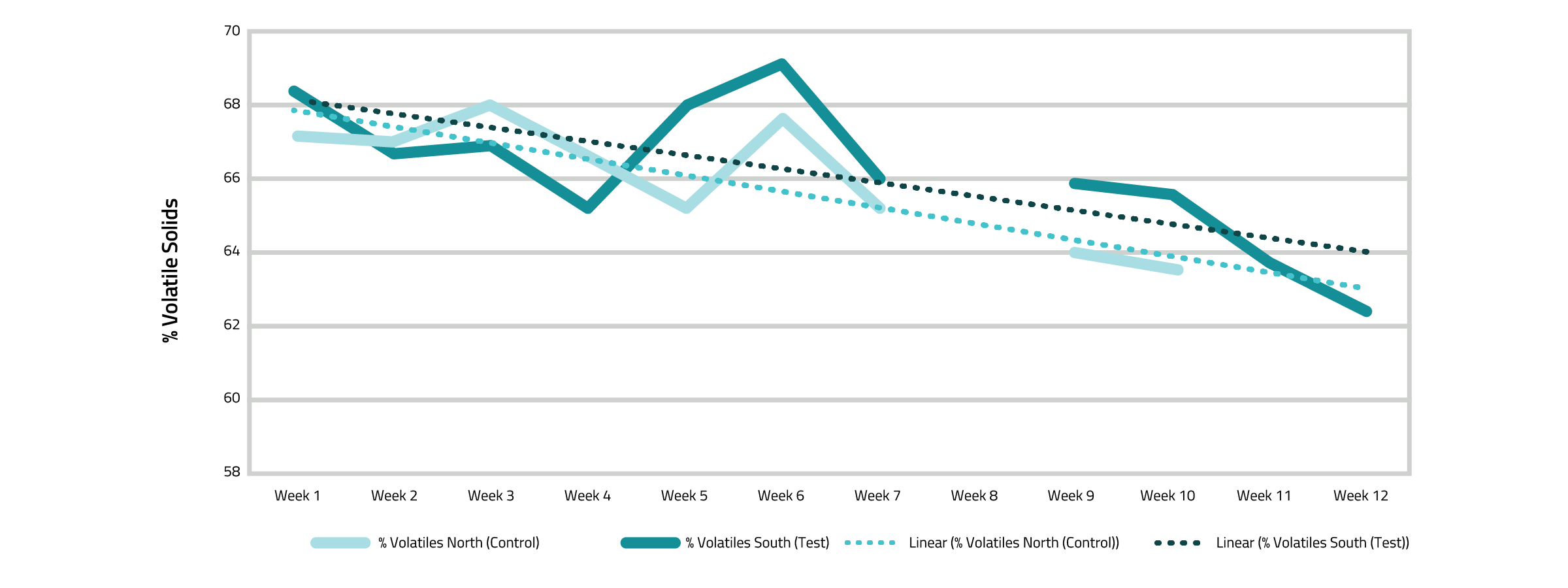
Fig 3. Pounds of Sludge Loaded, Cumulative
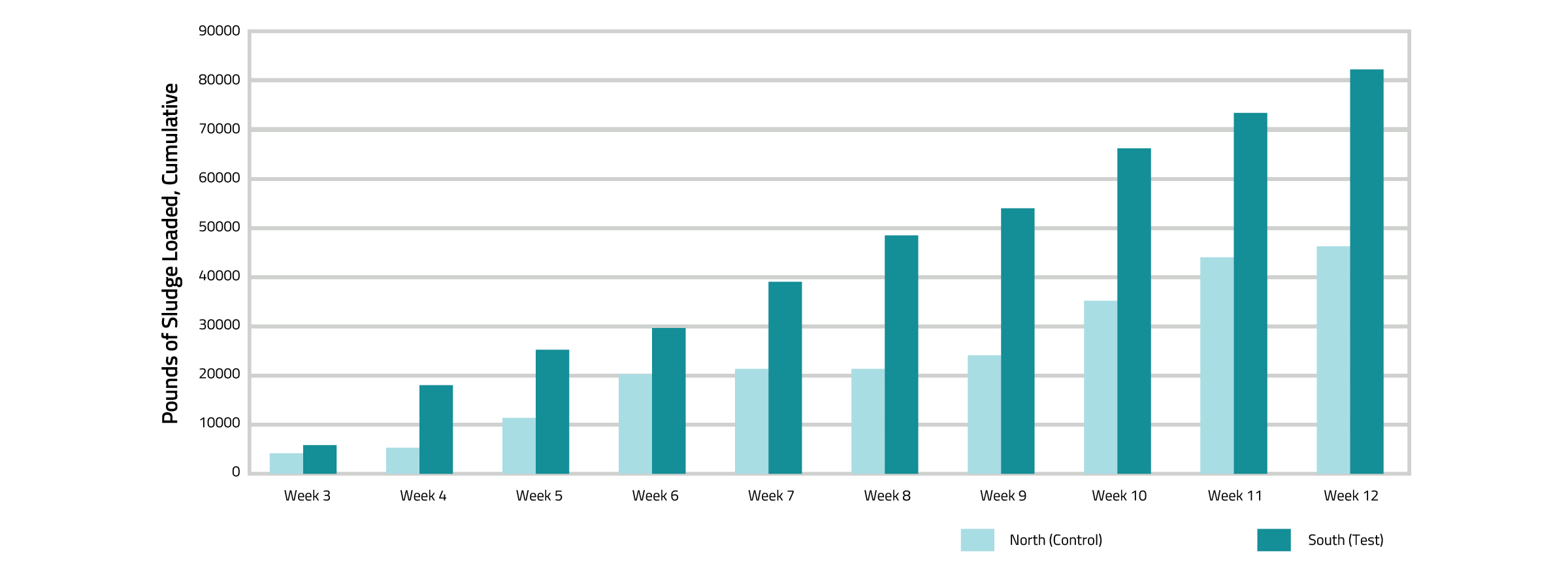
Conclusion
The OUR between the North and South Digesters showed no significant difference in this study. However, it is important to note that the South Digester received nearly twice as much sludge over the 12-week test period. The performance of the South Digester suggests the addition of Qwik-Zyme D improved the metabolic health of the bacteria and mitigated the expected negative impact of the additional loading. Most importantly, the South Digester achieved an impressive 59.85% reduction in sludge, suggesting that this significant decrease was due to the combined effects of operational changes and the addition of Qwik-Zyme D.
