Ana-Zyme G
Ana-Zyme G is a blend of concentrated enzymes formulated to quickly reduce fats, oils, and grease in anaerobic digesters and lagoons, preventing issues like grease caps and foaming. Ana-Zyme G targets triglycerides and long-chain fatty acids; including linolenic, oleic, stearic, and palmitic acids, as well as fish oils, dairy fats, and egg fats; to convert them into short-chain fatty acids. The production of short-chain fatty acids is crucial for the acidogenesis–methanogenesis process that drives gas production.
Rapid Fat, Oil, and Grease Reduction: Quickly breaks down fats, oils, and grease in anaerobic digesters and lagoons.
Prevents Grease Caps and Foaming: Helps avoid operational issues like grease caps and foaming in anaerobic digesters.
Breaks Down a Wide Range of Fats: Effective on fatty acids like linolenic, oleic, stearic, and palmitic, as well as fish oils, triglycerides, dairy, and egg fats.
Supports Acidogenesis Process: Promotes the production of short-chain fatty acids, essential in the acidogenesis-methanogenesis process.
$212.00 – $8,715.00
Rapid Fat, Oil and Grease Reduction:Quickly breaks down fats, oils, and grease in anaerobic digesters and lagoons.
PRevents Grease Caps and Foaming: Helps avoid operational issues like grease caps and foaming in anaerobic digesters.
Breaks Down a Wide Range of Fats: Effective on fatty acids like linolenic, oleic, stearic, and palmitic, as well as fish oils, triglycerides, dairy, and egg fats.
Supports Acidogenesis Process: Promotes the production of short-chain fatty acids, essential in the acidogenesis-methanogenesis process.
| Anaerobic Digester or Anaerobic Lagoon | ||
|---|---|---|
| Initial Dose (Daily for 1 month) | Maintenance Dose (Daily after 1 month) | |
| 2.5 Gal per 500,000 Gal Digester Volume | .5 Gal per 100,000 Daily Inflow | |
Product Info
Ana-Zyme G is formulated to quickly reduce fats, oils, and greases in anaerobic digesters and lagoons, preventing issues like grease caps and foaming. The biocatalysts in Ana-Zyme G targets triglycerides and longchain fatty acids; including linolenic, oleic, stearic, and palmitic acids, as well as fish oils, dairy fats, and egg fats; to convert them evenly into shortchain fatty acids. The production of short-chain fatty acids is crucial for the acidogenesis–methanogenesis process.
Ana-Zyme G is designed to limit volatile acid accumulation, while also increasing biogas generation. Additionally, Ana-Zyme G prevents the accumulation of undegraded fats in a system, which enhances volatile solids destruction, particularly in systems with limited mixing, such as lagoons.
The Science Behind
Ana-Zyme G is formulated to provide immediate reduction of fat, oil, and grease in anaerobic digesters and lagoons to avoid issues with grease caps and foaming. The biocatalysts in Ana-Zyme G rapidly speed the breakdown of complex fat molecules into simple short-chain fatty acids which then break down to acetic acid, a compound used in methanogenesis.
The goal of this product is to limit volatile acid accumulation, while also increasing biogas generation, and improving volatile solids destruction.
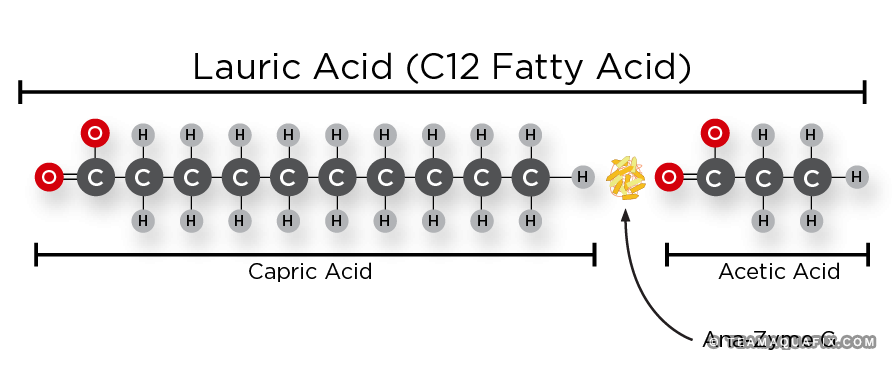
Ana-Zyme G can degrade a range of fatty acids such as linolenic, oleic, stearic, and palmitic as well as fish oils, triglycerides, dairy, and egg fat. The production of short-chain fatty acids is very important as part of the acidogenesis–methanogenesis process.
High Levels of Grease in Anaerobic Digesters
FOG must undergo several steps to be converted into the ideal food substrate for methanogens, acetate: disintegration, hydrolysis, and β-oxidation.
Limitations in the rates of any of these steps can lead to uneven degradation of FOG, which results in variable volatile acid loading on methanogens. Variable loading of volatile acids can easily overwhelm methanogens leading to accumulation of volatile acids, eventually resulting in a drop in digester pH. These impacts are exacerbated in systems with high FOG loading.
However, FOG can be made into an excellent food substrate for anaerobic digestion, due to their high COD content, as well as their high potential to generate large quantities of acetate or acetic acid. It just needs a little processing to get there.
Ana-Zyme G and Anaerobic Grease
Ana-Zyme G acts as a catalyst to naturally occurring bacteria to aid in the breakdown of FOG, which prevents the overloading of methanogens and frees up this new food source. Ana-Zyme G does this by targeting triglycerides and long-chain fatty acids to convert them evenly into short-chain fatty acids. This stabilization of fatty acid degradation allows methanogens to better acclimate to fatty acid loading. They are then able quickly uptake these fatty acids, reducing the chances of volatile fatty acid accumulation. In addition, Ana-Zyme G prevents the accumulation of undegraded fats in a system, which enhances volatile solids destruction, particularly in systems with limited mixing such as lagoons.
Product Pairings
Pair with BioGas1 to increase biogas production.

